Let’s face it. Turtles Need Advocates.
Turtles need people who love them to speak up for them, and to advocate for protection of their wild habitat.
Turtles around the globe are struggling with habitat loss and fragmentation, poaching, and altercations with man made machinery, and they all face an uncertain future. Sadly, our native box turtles seem to have been totally forgotten about.
Up and down the east coast, the Interstate 95 corridor, from the first colonist to the present day neighborhoods, we have been destroying woodland habitat. All of our native creatures have been affected by this loss of shelter and food, some have adapted better then others, even learning to exploit our carelessness, others, succumb to the heavy equipment that removes the trees, plowing the earth in its wake.
The defenses that have evolved in our Eastern Box Turtles, have served them well for millions of years. These Turtles evolved with a hinge, putting them in a very unique and special group of Chelonians, and when danger approaches, they have the ability to close themselves up into their bone hard shell, making themselves impenetrable to all but the largest predators. Their colorful unique markings on their shell help them blend into the filtered light and colorful leaves of their forest floor home and avoid detection.
There was a time when the forests our box turtles called home spread all along the east coast, now these forests are divided by highways, cities, housing developments and industrial sites, So it is not hard, for many of us, when we come upon such a unique and amazing creature, to want to help it continue to survive. Sometimes moving them across the road, as we are all told to do, may not be the best option. A destroyed habitat often spreads and surviving turtles are indeed lost. Sometimes an “across the road” is a new apartment complex. This “problem” is very complicated, as turtles are hard to relocate due to their attachment to their native home where they learn the topography, the food, water sources and best hides. Moving box turtles to a new location leaves them searching for familiar landmarks and they often will traverse miles, crossing unfamiliar territory looking for home. Moving turtles can also expose populations to pathogens that can be devastating to existing populations.
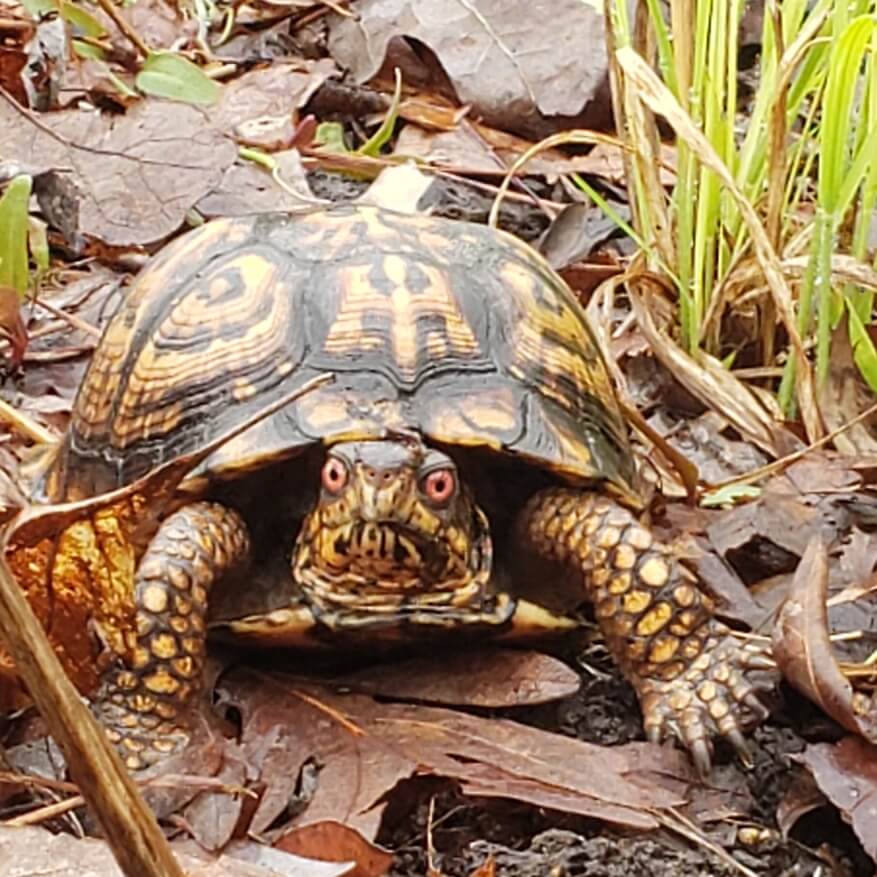

This is Oscar. Oscar was found at the bottom of a trash can, at a gas station of off Interstate 95, in the City of Richmond VA. Because Oscar has three legs, it is assumed that he was tossed by the poachers that were transporting him.
Furthermore, in an attempt to curb illegal poaching, laws in many states have made it illegal to own our native Eastern box turtles with out a permit, nor can they be adopted out. Some States requiring Euthanasia for unwanted pets and turtles that have lost their habitat due to human encroachment.
The Glass Box
So here we are. What now? So you took that turtle home 15 years ago. You kept a wild creature in a glass box. An animal that would normally travel through a territory possibly many miles every year. You kept him by a window, least he forget what the sun looked like and you fed him things that you thought he should eat. No slugs, very few worms, no beetles, carrion or wild berries. And now keeping this turtle is inconvenient and you realize that you have not done him any favors. The color of his shell is brown. There are no colorful markings. His nose is short and his beak is overgrown, giving him an overbite. His tail is nonexistent, as it basically disappeared from years of living on that dry bark mulch they sold you at the pet store, and his nails are growing in circles from lack of a natural movement. If he is lucky, he is not suffering from Metabolic Bone Disease. A devastating result caused from the inability to process nutrients, due to improper diet, housing and lighting

So you begin to search for a solution for your ill begotten pet, a new home, a chance for your turtle to live his best turtle life, and this is what you learn:
Finding someone that both is legally allowed to house box turtles through their states wildlife department and, has the room to take your turtle, is difficult at best.
If your turtle is a male, it could take years of carefully orchestrated behavior modification to get him to the point that he can be housed with other turtles. I can barely imagine how it would feel to be snatched away from the world I know and be put into a glass box with a small dish of water, and some unfamiliar food. How long would it take for me to quite trying to climb out of the corner, and eventually just hide in my shell, Day in, Day out. I am quite positive I would be pretty confused, angry and defensive after 15 years of solitary confinement. Building adequate outdoor housing for each of these turtles is unrealistic even for the best of sanctuaries. Females recover from incarceration a little better, and seldom exhibit the aggressive fighting behavior that males in captivity do.
Once taken home and kept as a pet, YOU are responsible for that pet. period. Dog, Cat, Gerbil, Snake, Horse, Turtle.. what ever the pet is. It is a life that now depends on you to do the right thing and provide for it in the best possible humane way. That also means that you are responsible for veterinary care, and yes there are exotic vets that can help you keep your turtle healthy and happy. Turtles are connected and are part of the earth that they evolved with. If you cannot keep them outside in a natural habitat, then you will have to have plenty of room indoors to build an adequate habitat that includes a water hole big enough for your turtle to climb in and soak, hides, proper lighting that mimics the sun through out the year and offers them variant temperatures and a wide assortment of native and natural foods that are appropriate for the age of your turtle .
Knowing how few options there are for turtles to find sanctuary, it is VERY difficult for those of us that run sanctuaries to turn away turtles in need. While you think your turtle may need a home, there are as many stories of lost and found turtles that once were wild, and are now homeless, and are facing euthanasia, just because someone bulldozed their habitat.
Unfortunately, turtles that have been in a tank for 15 years usually need a slow reacclimating to outside living, depending on how much damage has been done. Can they close their shell tight? Will they be able to brumate? Can they catch live food? Are they aggressive to others?
Box Turtles can live well over 100 years. When you do find a sanctuary that is willing to take your 15 yr pet and possibly provide for it for the next 50? 75? 100 years, what is this worth to you?
250 million years, Turtles have been on this planet. As a species, Humans certainly could learn a lot about our earth from these small dinosaurs of our woodlands. How to adapt, How to get along, how to heal, share and survive. Box turtles are quite amazing. They are personable and unique. Their super powers far outnumber ours and if they can survive this human invasion, they will have survived it all.
Please help keep turtles in the wild. Protect wild spaces! Plant native and beneficial Plants, make your yard turtle and wildlife friendly, and most important SPEAK UP. LEAN IN.. Spread the word and advocate, to your local and state representatives, your neighbors, friends, anyone that will listen.
It is time!
It is never too late to Do the Right Thing
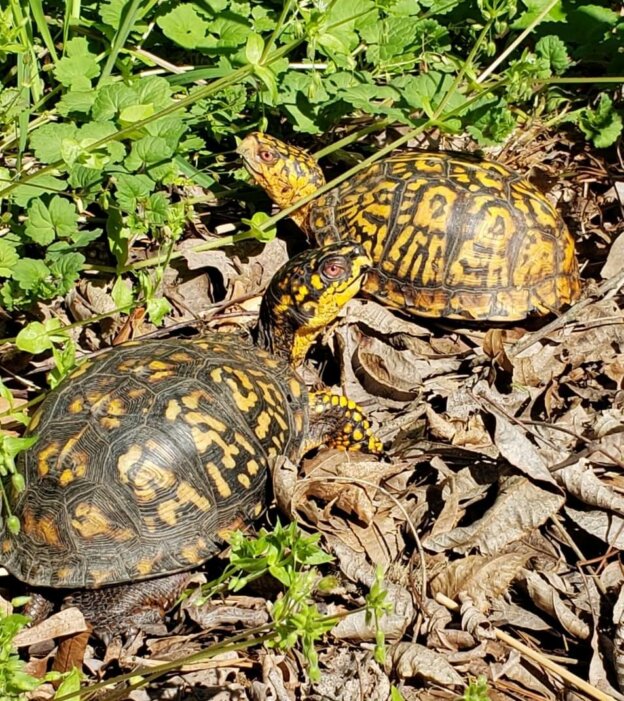









 this allows the nest temperatures to remain stable and the cavity gives the babies room to dig out. The Mother turtle will carefully bury her eggs and with unbelievable skill, will place a final layer of leaves or mulch on top, which will make the nest almost indiscernible to the average eye, once completed, the mother turtle abandons the nest. The eggs, and hatchlings are left on their own.
this allows the nest temperatures to remain stable and the cavity gives the babies room to dig out. The Mother turtle will carefully bury her eggs and with unbelievable skill, will place a final layer of leaves or mulch on top, which will make the nest almost indiscernible to the average eye, once completed, the mother turtle abandons the nest. The eggs, and hatchlings are left on their own. The loss of natural and native habitat is causing turtles to appear in some unlikely places. Mother turtles of all kinds may walk far from their home to find the perfect site to dig their nest, often crossing roads and lawns on their journey. Many times, due to man-made altercations to the landscape, baby turtles appear where one least expects them, and unfortunately, there is not always a suitable habitat nearby that could sustain a viable population.
The loss of natural and native habitat is causing turtles to appear in some unlikely places. Mother turtles of all kinds may walk far from their home to find the perfect site to dig their nest, often crossing roads and lawns on their journey. Many times, due to man-made altercations to the landscape, baby turtles appear where one least expects them, and unfortunately, there is not always a suitable habitat nearby that could sustain a viable population.



 Help Support The Box Turtle Sanctuary every time you shop at Kroger!
Help Support The Box Turtle Sanctuary every time you shop at Kroger!












 A rehabber, is someone who takes care of those that are recovering from a specific condition, to fix it up and make it better. Often times when someone mentions rehab, we think of drug or alcohol abuse and the process it takes to “get off the wagon”.
A rehabber, is someone who takes care of those that are recovering from a specific condition, to fix it up and make it better. Often times when someone mentions rehab, we think of drug or alcohol abuse and the process it takes to “get off the wagon”.







